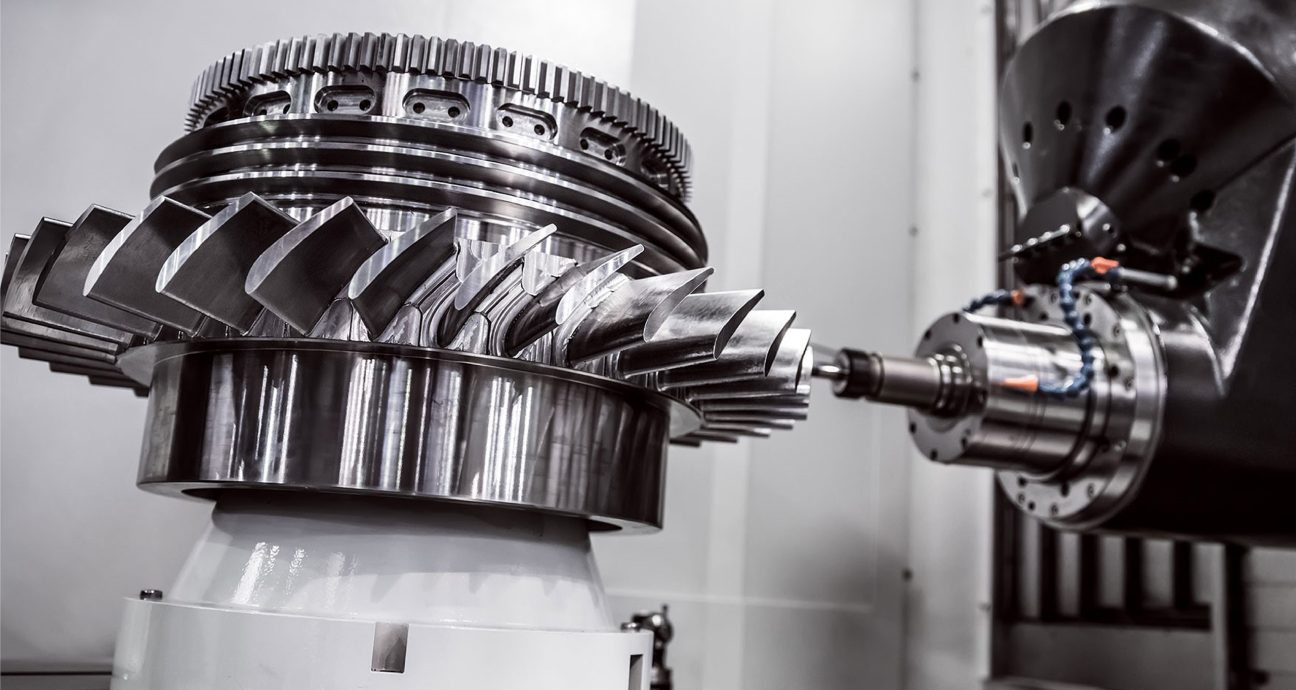
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is an advanced manufacturing technology where machines and tools are controlled by computer programs to perform operations such as cutting, milling, turning, drilling, grinding, and shaping materials with high precision. This represents a significant leap from traditional machining methods, offering superior efficiency and quality. CNC technology has become a cornerstone of modern industry, widely used in fields such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, healthcare, and construction.
CNC Machining Process
The CNC machining process typically involves the following steps:
- 3D Model Design
The process begins with designing the product using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. A 3D or 2D model is created to define the shape, dimensions, and technical specifications of the component. - CAM Programming
The model is then transferred to CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software for programming. CAM generates command codes (G-code or M-code) that instruct the CNC machine on how to perform machining operations. - Data Transfer to CNC Machine
The command codes are uploaded to the CNC machine’s controller. Operators review, fine-tune, and ensure the program is accurate before initiating the machining process. - Machining Process
The CNC machine uses cutting tools (e.g., milling cutters, drill bits, lathes) to cut, grind, and shape the material based on the program instructions. This process is fully automated, enabling the production of complex components with high precision.
Advantages of CNC Machining
- High Precision and Quality
CNC technology enables the creation of components with minimal errors, often within micron-level tolerances. This is crucial for industries requiring stringent standards, such as aerospace and healthcare. - High Automation
CNC machining minimizes human intervention, reducing errors caused by manual operations while improving efficiency and lowering labor costs. - Flexibility in Design and Production
With CNC, complex and diverse components can be manufactured by reprogramming the machine, eliminating the need for manual tool changes. - Increased Productivity
CNC machines can operate continuously 24/7, allowing rapid mass production while maintaining consistent quality. - Reduced Material Waste
CNC optimizes cutting processes, minimizing material wastage and lowering raw material costs while reducing environmental impact. - Easy Integration with Technologies
CNC machines can integrate with other technologies, such as laser cutting, 3D printing, and robotics, enhancing versatility and production efficiency.
Applications of CNC Machining
CNC machining is widely applied across various industries, including:
- Automotive: Manufacturing engine components, shafts, gears, and transmission systems with high precision.
- Aerospace: Producing critical parts such as turbine blades, airframes, and navigation systems.
- Healthcare: Fabricating surgical instruments, medical devices, and bio-implant components.
- Electronics: Creating compact components like circuit boards, casings, and electronic devices.
- Construction: Producing metal structures, molds, and components for construction machinery.
Challenges and Development Trends
Challenges:
- High Initial Investment: CNC machines and associated software require significant upfront and maintenance costs.
- Technical Expertise Required: Operators must have in-depth knowledge of programming and mechanical engineering.
- Industry Competition: As CNC becomes more prevalent, businesses must continually innovate to maintain a competitive edge.
Development Trends:
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI optimizes programming and operations, enhancing precision and efficiency.
- IoT Connectivity: Connecting CNC machines to IoT networks enables remote monitoring and control, improving production management.
- New Material Applications: Research is advancing the ability to machine complex materials like composites and advanced alloys.
Conclusion
CNC machining is not just a significant advancement in manufacturing but also a catalyst for innovation across numerous industrial sectors. With advantages in precision, automation, and adaptability, CNC has become the ideal solution for modern production needs. The continued development of CNC technology promises to drive innovation and efficiency in the global economy.